The detection of Covid-19 coronavirus in Nigeria raised early concerns about the country’s capacity to handle a major epidemic but so far local public health officials have been commended for handling the outbreak with aplomb.
But the coronavirus is not the only viral outbreak in Africa’s most populous country. Nigeria is currently dealing with what is turning out to be the world’s largest epidemic of Lassa fever, a viral disease deadlier than coronavirus.
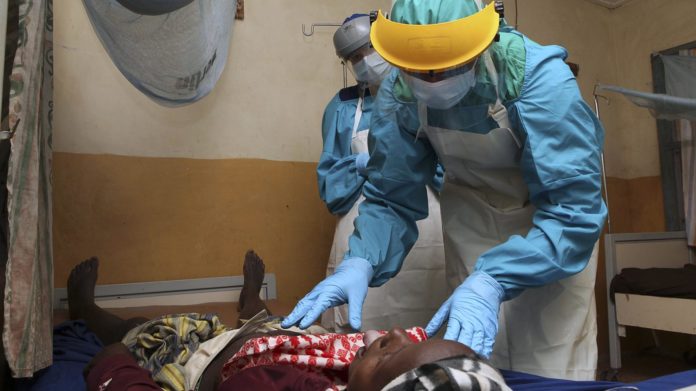
Lassa fever is a severe viral hemorrhagic fever (VHF) like Ebola and Marburg that occurs throughout the year in Nigeria and was declared an “active outbreak” by the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) five weeks into 2020. The epidemic which occurs during the annual dry season (roughly November through March) has spread across half the country.
The Lassa fever virus is transmitted to humans through contact with food or household items contaminated with urine and feces of a rat. It’s also known to spreads from person-to-person through contact with the body fluids and organs of infected persons, which has resulted in healthcare workers easily getting infected, some have died.
The epidemic, whose rapid escalation started right from the second week of the year, had by the end of the ninth week seen 774 cases and 132 deaths spread across 26 of Nigeria’s 36 states and the federal capital territory.
Troubling trends
In the past five years, there have been four epidemics—all having over 59% of total cases—in the first quarter of the year. In just nine weeks into 2020 Lassa fever cases are already 96% of total cases in 2019, the year with the largest Lassa epidemic with 810 cases and 167 deaths. As recently as 2015, the total number of cases was 64. This trend does not only suggest that the current epidemic will likely surpass that of 2019, but it also suggests a longer lasting and more devastating epidemic.
Arenaviruses, which include the Lassa virus, are disproportionately prone to genetic mutations and have a propensity for spread if not adequately controlled, says Dr Olubusuyi Moses Adewumi, a specialist in Arenaviruses and Virologist at the College of Medicine, University of Ibadan in southwest Nigeria.